Drone Technology in India – Economic Potential, Policy Framework, and Future Prospects
Drone technology periodically features in UPSC GS Paper 3 (Economy, Science & Technology, Infrastructure) and in essay or interview themes on innovation-driven growth, industry policy, and employment generation. Aspirants should be able to analyze how drones can spur economic transformation, the contours of India’s regulatory efforts, and the balance between opportunity and challenges for the sector.
Introduction
Drone technology, also known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), refers to aircraft systems that operate without a human pilot onboard and are either remotely controlled or autonomous. In India, drones are gaining prominence across economic and technological fields due to their versatility, precision, and capacity to access remote or hazardous areas. Their integration with “Industry 4.0″—the ongoing digital transformation encompassing IoT, AI, and automation—shows drones are becoming integral to India’s push for innovation-driven growth, digital governance, and efficient service delivery.
Understanding Drone Technology
Types of Drones
- Nano Drones: Less than or equal to 250 grams; used for hobby, early education.
- Micro Drones: 250 grams to 2 kg; simple tasks like photography, security.
- Small Drones: 2 kg to 25 kg; agriculture, mapping, industrial inspection.
- Medium Drones: 25 kg to 150 kg; logistics, government projects.
- Large Drones: Above 150 kg; heavy-duty delivery, military operations.
Working Principles
- Remotely Piloted: Operators directly control the drone (common in civil and many defense applications).
- Autonomous Drones: Use pre-programmed instructions, GPS, AI, and sensors to operate independently.
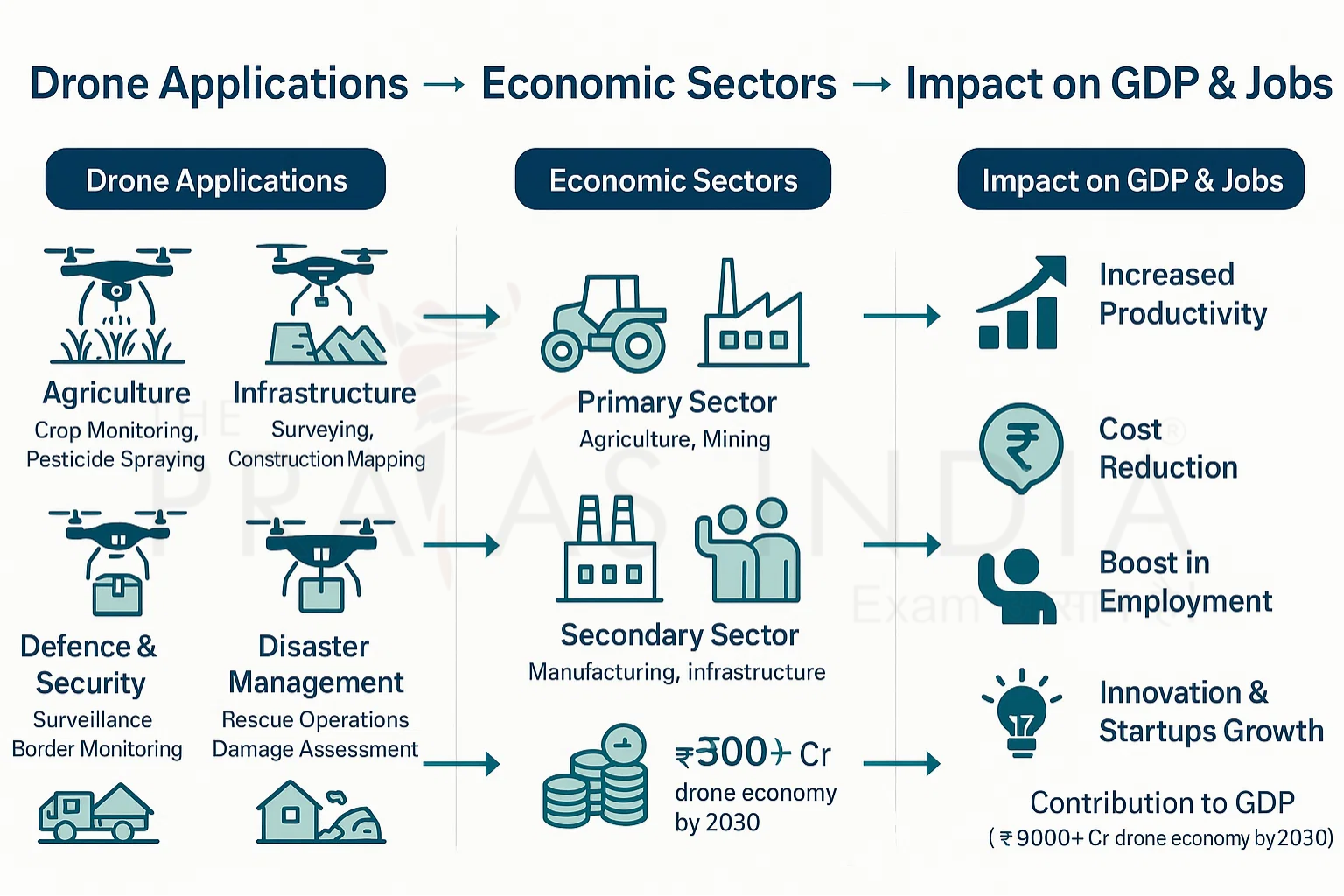
Major Applications
Globally and in India, drones are being utilized by:
- Agriculture: Crop monitoring, pesticide spraying, yield estimation.
- Infrastructure & Mining: Land surveying, 3D mapping, site inspections.
- Logistics & E-commerce: Last-mile deliveries, inventory management.
- Disaster Management: Flood, earthquake, and damage assessment, rescue logistics.
- Urban Planning & Real Estate: 3D city models, construction monitoring.
- Defense & Security: Surveillance, crowd management, border security.
- Media & Entertainment: Aerial shots for films, events, journalism.
Economic Significance of Drones
Drones are transforming sectoral productivity, unlocking new revenue streams, and enabling efficient resource utilization:
- Agriculture: Precision drones improve yields and cut costs[citation_id], increasing farm incomes (see Namo Drone Didi Scheme impact).
- Infrastructure: Faster, more accurate inspection reduces delays and enhances safety.
- Logistics: Drones enable rapid, contactless delivery, crucial in remote/rural areas during emergencies.
- Disaster Management: Quicker damage mapping, targeted relief drops, and reduced risk to personnel.
The proliferation of drones has ripple effects in:
- Job Creation: Pilots, analysts, hardware techs, repair, software developers.
- Startup Ecosystem: Surge in Drone-as-a-Service platforms, indigenous manufacturing, and local innovation.
- Market Size: India’s drone market was valued at $1.21 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $2.58 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of ~8.8%. Another source puts India’s drone market at $1.39–1.58 billion in 2025, expected to rise rapidly by 2030 at over 17–20% CAGR.
- GDP Contribution: While still small, the sector’s compound effect across industries and its potential to become a $10 billion industry make it a key driver for future growth.
Major Drone Policies and Schemes
| Policy/Scheme | Year | Objective/Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Drone Rules | 2021 | Liberalised regulation, simplified permission, expanded scope |
| PLI Scheme for Drones | 2021 | Incentives for manufacturing and component localization |
| Digital Sky Platform | 2021– | Online registration and NPNT operational clearance |
| Kisan Drone Scheme | 2022 | Drones for agriculture—training and financial support |
| SVAMITVA Yojana | 2021– | Property mapping in villages using drones |
| GST Reduction | 2025 | Uniform 5% GST to lower operating and capital costs |
| Drone Shakti/Skill initiatives | 2022+ | Startup incubation, pilot/technician skill-building |
Government Policies and Initiatives
The Indian government is actively fostering drone adoption and innovation:
1. Drone Rules 2021: These replaced restrictive older norms with:
- Seamless online application via the Digital Sky Platform
- Relaxed size and weight restrictions (now up to 500 kg, covering even drone taxis)
- Reduced documentation and approval hurdles, putting more focus on trust and self-certification
2. Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Drones (2021):
- Financial incentives for domestic manufacturing, aiming to reduce import dependency.
- Target segment includes both complete drones and critical components.
3. GST Reduction: Uniform GST rate lowered to 5% in 2025, ensuring affordability for businesses and startups.
4. Digital Sky Platform:
- Online portal for drone registration, flight permissions (No Permission, No Takeoff or NPNT compliance), and regulatory guidance.
5. Other Major Initiatives:
- Kisan Drone Scheme: Subsidies and training for farmers to use drones in agriculture.
- SVAMITVA Yojana: Mapping rural inhabited lands for property cards using drones.
- Defence Drone R&D: Boosting indigenous capabilities and self-reliance.
- Drone Shakti: Startup incubation and skill-building.
Role in India’s Economic Development
- Digital Governance: Drone mapping aids e-governance projects like digital land records and municipal planning.
- Smart Cities: Drones are integral for real-time infrastructure monitoring, mapping utilities, and surveillance.
- Logistics and Public Delivery: India Post trials, vaccine drops during COVID-19, and last-mile delivery pilots point to efficiency gains, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
- Startup and Innovation: More than 200 Indian drone startups are ushering in solutions for agriculture, logistics, and defense—making India a breeding ground for UAV innovation and entrepreneurship.
Challenges in the Drone Sector
Despite rapid growth, key roadblocks remain:
- Privacy and Security: Surveillance concerns, possible data breaches, hacking, and dual-use in terrorism/illegal activities.
- Airspace Management: Integrating drones safely into national air traffic requires robust UTM (Unmanned Aircraft Systems Traffic Management).
- Regulatory Awareness: Operators often lack full knowledge of law, compliance, or safety measures.
- Technology and Cost: High-quality sensors, batteries, and components are often imported, raising costs and limiting domestic value-add.
- Skill Shortage: Not enough trained UAV pilots, repair techs, or regulatory specialists.
Future Prospects and Global Comparison
Vision 2030 and India’s Drone Roadmap
- The government aims to make India a global drone hub by 2030, creating an enabling policy and incentive ecosystem.
- Over 29,500 drones registered as of early 2025, with Delhi, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra leading in adoption.
- Integration with AI, GIS, 5G, IoT, and cloud analytics will push drones into advanced use-cases such as precision farming, disaster prediction, climate monitoring, and defense automation.
Global Benchmarking
- USA: World leader in R&D investment and regulatory frameworks; home to major UAV firms.
- China: Dominates hardware manufacturing (DJI, largest market share globally), rapid consumer and commercial adoption.
- Israel: Innovator in military and security drone applications.
- India: Fastest-growing drone market in Asia-Pacific; aims to catch up by fostering local manufacturing, innovation clusters, and regulatory reforms.
Exam-Ready Fast Facts
- India’s drone market estimated at $1.21 to $1.58 billion (2024), projected to reach $2.6–4.8 billion by 2030 (CAGR: 8.8–20.4%).
- Over 29,500 drones registered as of Jan 2025, with Delhi, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra in lead.
- Key government policies: Drone Rules 2021, PLI scheme, GST rate cut to 5% in 2025.
- Focus sectors: Agriculture, Infrastructure, Logistics, Disaster Mgmt, Defence, Real Estate, Media.
- Major growth drivers: Digital transformation, Make in India, government incentives, startup boom.
- Critical challenges: Privacy, regulatory compliance, skilled workforce, import dependence.
- India aims to become a global drone hub by 2030; among fastest-growing markets in Asia-Pacific.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is drone technology and how does it operate?
A1. Drone technology involves Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) that are either remotely controlled or autonomous. They use sensors, GPS, and AI to perform tasks in various sectors without onboard pilots.
Q2. What are the major types of drones based on size?
A2. Drones are classified as Nano (≤250g), Micro (250g-2kg), Small (2-25kg), Medium (25-150kg), and Large (>150kg), with applications varying based on weight and capabilities.
Q3. How is drone technology important economically in India?
A3. Drones boost agriculture, logistics, infrastructure, disaster response, and surveillance, improving productivity and creating new jobs. India’s drone market is rapidly expanding, projected to become a multi-billion dollar industry by 2030.
Q4. What key government policies support drone industry growth?
A4. The Drone Rules 2021 simplify regulations; the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme promotes domestic manufacturing; Digital Sky Platform facilitates permissions; schemes like Kisan Drone and SVAMITVA enable application in agriculture and property mapping.
Q5. What challenges does India face in drone adoption?
A5. Privacy concerns, airspace management, cyber threats, lack of skilled manpower, high import dependency on parts, and affordability are significant hurdles.
Q6. How does India’s drone sector compare globally?
A6. India is one of Asia’s fastest-growing markets, aiming to become a global drone hub by 2030. It is behind leaders like the USA, China, and Israel but is advancing through policy reforms and innovation.
Q7. What future opportunities exist for drone technology in India?
A7. Integration with AI, GIS, 5G, and data analytics will expand drone applications to precision agriculture, smart city management, disaster prediction, and defense, transforming multiple sectors.