Global Innovation Index (GII) – Measuring Innovation and India’s Performance
The Global Innovation Index is frequently featured in UPSC Prelims (reports, indices, rankings) and Mains GS Paper 3 (Economy, Tech, Growth, and Development), as well as in essay and interview discussions focusing on innovation-driven growth and sustainability. Knowledge of India’s GII rank, strengths, weaknesses, and policy implications is crucial for producing data-backed answers and insightful analysis in the exam context.
Introduction
The Global Innovation Index (GII) is a comprehensive global ranking framework used to measure and compare the innovation capacities and outcomes of countries. Published annually by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) in partnership with Cornell University and INSEAD, the GII provides insightful analysis covering over 130 economies, making it a critical benchmark for innovation in the global economy. For policymakers, investors, and researchers, the index is a guiding beacon, highlighting innovation-enabling strengths and barriers—directly impacting competitiveness, growth, and sustainable development.
Historical Background
Established in 2007, the GII responded to the need for a multifaceted global metric that goes beyond just R&D expenditure and patent counts. Its founders recognized that innovation is shaped not only by scientific research but also by institutions, human capital, infrastructure, and more. Since its inception, the GII has expanded both in depth and coverage, now in its 18th edition (2025). It reflects the evolving nature of knowledge economies, where intangible assets, digitalization, and creative industries play growing roles. The GII is now an essential tool for countries seeking evidence-led development strategies, especially those aspiring to leapfrog traditional pathways.
Methodology and Parameters
Overview of Calculation
The GII relies on a sophisticated framework built around two major indices:
- Innovation Input Index (5 pillars): Measures the environment and resources available for innovation.
- Innovation Output Index (2 pillars): Evaluates tangible results produced by innovation activities.
The 7 Pillars of GII
Inputs:
- Institutions (government, regulatory quality, business climate)
- Human Capital & Research (education system, researchers, R&D spend)
- Infrastructure (ICT, general utilities, ecological sustainability)
- Market Sophistication (credit, investments, trade openness)
- Business Sophistication (knowledge workers, clusters, partnerships)
Outputs:
6. Knowledge & Technology Outputs (patents, publications, technology transfer)
7. Creative Outputs (branding, creative goods/services exports, intangible assets)
A total of 78 indicators are used, drawing on international databases such as the World Bank, UNESCO, and ITU. The methodology continues to evolve, now integrating geospatial analysis and sub-national metrics, which allows assessment of innovation clusters within countries.
| Pillar | Type | Sample Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Institutions | Input | Regulatory quality, ease of business |
| Human Capital & Research | Input | School enrollments, R&D intensity |
| Infrastructure | Input | Energy access, ICT adoption |
| Market Sophistication | Input | Venture capital records, trade policies |
| Business Sophistication | Input | Knowledge workers, collaboration metrics |
| Knowledge & Technology Outputs | Output | Patent filings, tech exports |
| Creative Outputs | Output | Brand value, design exports |
Global Rankings and Key Insights
2025 GII results reveal a nuanced global innovation map:
- Switzerland continues its reign at the top for the 15th year, excelling in creative outputs, business sophistication, and knowledge intensity.
- Sweden (2nd) and USA (3rd) form the leading trio, with Sweden leading in research and creative outputs; USA leading in business sophistication and venture capital activity.
- South Korea rises to 4th, topping pillars like Human Capital & Research and R&D expenditure.
- Singapore holds 5th, with global leadership in government effectiveness and high-tech manufacturing.
- China makes its debut in the top 10, becoming the world leader in patent filings, knowledge and technology outputs, and hosting the most innovation clusters (including Shenzhen–Hong Kong–Guangzhou and Beijing).
Innovation is increasingly concentrated in regional clusters—Silicon Valley, Shenzhen, Stockholm, and Delhi–Bangalore—while Asia and Africa see fast movers like China, India, Vietnam, and Morocco.
Top 10 countries (2025):
| Rank | Country | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Switzerland | Top in creative outputs |
| 2 | Sweden | Leading in researchers |
| 3 | USA | Top in venture capital |
| 4 | South Korea | R&D expenditure, education |
| 5 | Singapore | High-tech manufacturing |
| 6 | UK | Startup ecosystem |
| 7 | Finland | Digital infrastructure |
| 8 | Netherlands | Creative industries |
| 9 | Denmark | Government online services |
| 10 | China | Patent powerhouse |
India’s Performance in GII
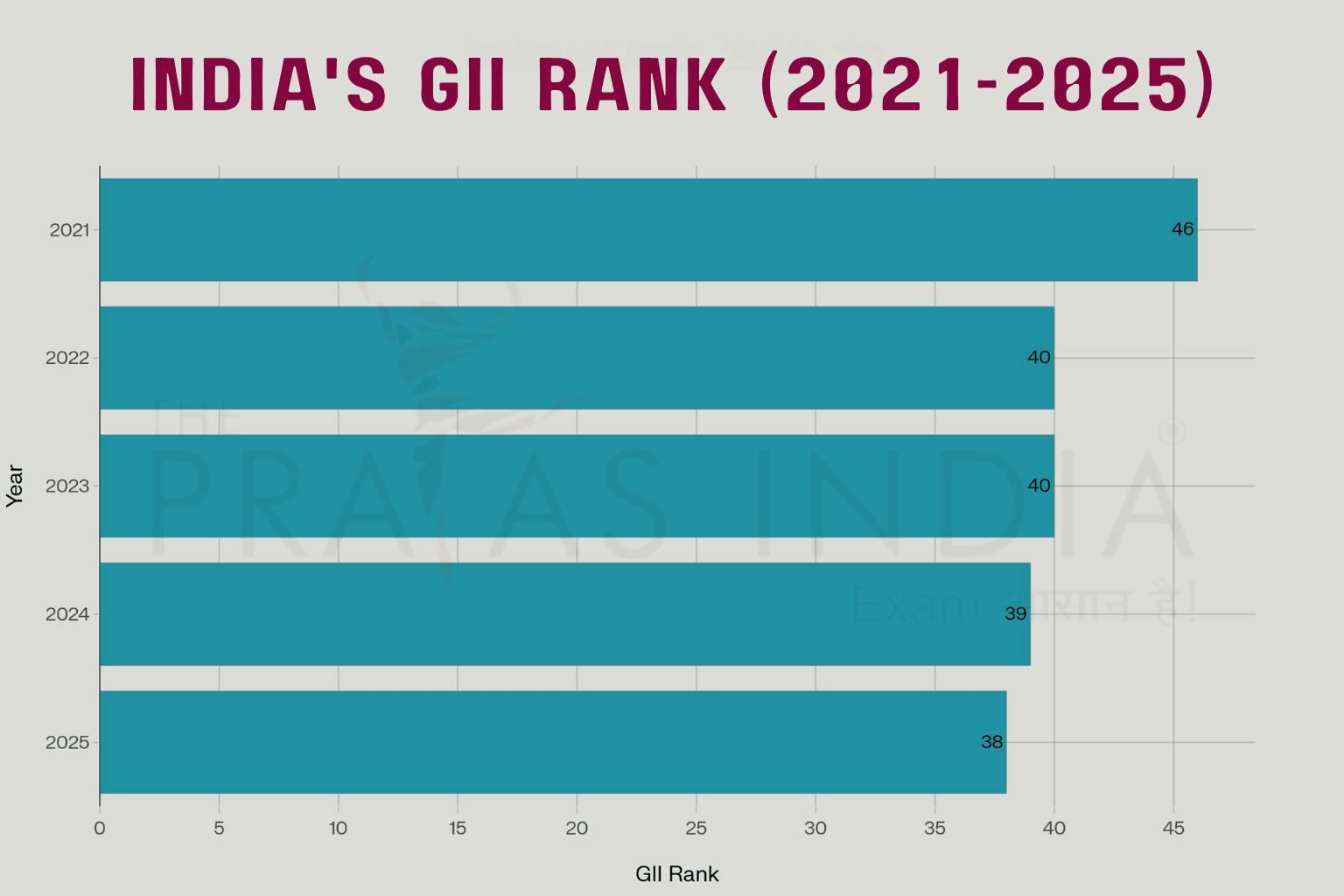
India’s global innovation trajectory continues to rise:
- India ranks 38th in 2025, leading Central & Southern Asia, outperforming all other lower-middle-income economies.
- Strengths:
- ICT services exports (1st globally) and unicorn (startup) valuations (11th)—showing growth in the digital economy.
- Knowledge & Technology Outputs (22nd): Increased patents, scientific & technical publications, robust tech startups.
- Market Sophistication (38th): Improvements in venture capital, credit, international investment.
- Business landscape marked by the rise of innovation clusters—Bengaluru, Delhi NCR, Mumbai, Chennai.
- Weaknesses:
- Gaps in business sophistication (64th), sectoral linkages between academia and industry, and the scale/impact of applied research.
- Infrastructure challenges (61st): Limited universal energy access, digital divides, and sustainability issues.
- Institutional quality (58th): Regulatory environment, public sector governance needs progress.
Government initiatives such as Startup India, Atal Innovation Mission, Digital India, Make in India, and targeted policies are driving a vibrant entrepreneurship ecosystem. India leads among lower-middle-income economies for 15 years, outperforming peers consistently across the seven GII pillars.
Significance of GII for India
The GII acts as both a mirror and a catalyst:
- Helps policymakers diagnose innovation bottlenecks and strengths.
- Facilitates alignment of national priorities with economic reforms needed for knowledge-driven growth.
- Informs the design of new policies, investments, and regulatory changes to foster inclusive innovation.
- Empowers India’s journey to become a global innovation hub by spotlighting progress and gaps, vital for demographic dividend realization and job creation.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite progress, India faces deep-rooted challenges:
- Low R&D investment: At just 0.65% of GDP, India lags behind global leaders who invest 2–4%.
- Brain drain and skill gaps: Top talent migrates abroad, and domestic skill development is insufficient for deep-tech growth.
- Limited academia-industry collaboration: Need for more translational research, startup-university partnerships, incubation hubs.
- Intellectual property (IP) and regulatory reforms: Slow patent processing, enforcement gaps, and complex regulatory regimes.
- Digital and physical infrastructure: Bridging digital divides, ensuring universal energy and internet access is critical.
Policy Recommendations:
- Raise public-private R&D investment and incentivize corporate research.
- Foster innovation clusters and localize GII metrics to region/city levels with WIPO toolkit.
- Make IP ecosystem world-class for easier registration and fast enforcement.
- Accelerate skills initiatives, vocational programs, and STEM education.
- Strengthen academia-industry partnerships through joint labs, technology parks, and grant schemes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the Global Innovation Index (GII)?
A1. The GII is an annual ranking published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), in collaboration with Cornell University and INSEAD, assessing countries based on their innovation capacities and outcomes across more than 130 economies.
Q2. Why is the Global Innovation Index important?
A2. It serves as a benchmark for nations to evaluate their innovation performance, design policies for inclusive growth, and identify areas like education, infrastructure, and technology needing improvement.
Q3. How is the GII calculated?
A3. The GII measures innovation through two main indices – the Innovation Input Index (institutions, human capital, infrastructure, markets, business sophistication) and the Innovation Output Index (knowledge & technology outputs, creative outputs).
Q4. What was India’s rank in the Global Innovation Index 2025?
A4. India ranked 38th globally in the 2025 edition of the GII, maintaining its top position among Central and Southern Asia nations and lower-middle-income economies.
Q5. Who are the top performers in GII 2025?
A5. The top five countries are Switzerland, Sweden, the USA, South Korea, and Singapore, with China entering the top ten for the first time.
Q6. What are India’s strengths and weaknesses according to the GII 2025?
A6. India’s strengths include ICT services exports, a robust startup ecosystem, and knowledge creation, while challenges persist in infrastructure, regulatory quality, and industry-academia collaboration.
Q7. How does the GII help India’s policymaking?
A7. The GII informs strategic government initiatives like Startup India, Digital India, and Atal Innovation Mission, guiding investments in research and innovation-led economic reforms.
Q8. What is the significance of innovation for India’s economic growth?
A8. Innovation is crucial for technological self-reliance, job creation, sustainable development, and enhancing India’s competitiveness in the global knowledge economy.








