GRAP-IV Activation in Delhi–NCR (15 December 2025): Causes, Provisions, Impact & Exam Relevance
By The Prayas India Team
Best UPSC Coaching in Mumbai | Stay Updated with Daily Current Affairs
- UPSC/State PCS: Links to GS-III (Environment Pollution, Disaster Management) and GS-II (Governance, Federalism). Essay topics: “Air Pollution: Governance Challenge”.
- SSC/Banking: Covers Environment & Current Affairs sections; schemes like NCAP.
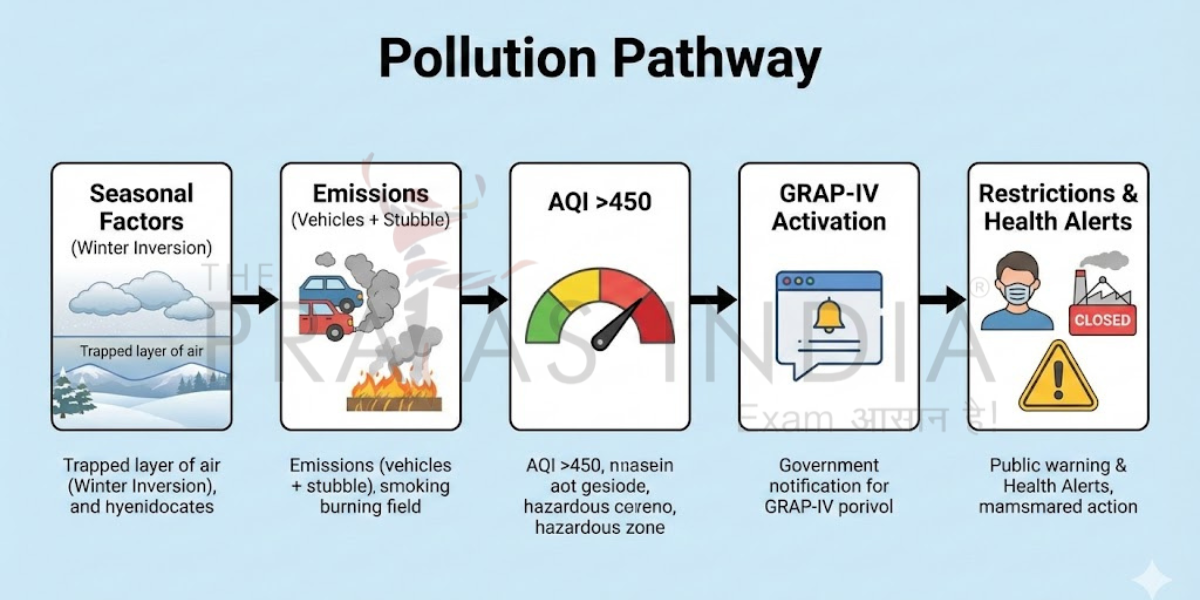
Delhi-NCR faces severe air pollution every winter, with smog reducing visibility and harming health. On 15 December 2025, the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) activated GRAP Stage IV as the Air Quality Index (AQI) crossed into the ‘Severe Plus’ category. This emergency step highlights governance challenges in balancing public health and economic needs.
What is GRAP?
The Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) is a set of emergency measures to combat air pollution in Delhi-NCR. Launched in 2017, it aims to reduce pollutants like PM2.5 and PM10 when AQI worsens. The CAQM oversees implementation, with support from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and state governments. It draws legal authority from the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Stages of GRAP
GRAP has four stages based on AQI levels. The table below outlines each stage’s measures.
| Stage | AQI Range | Key Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I: Moderate | 101–200 | Ban on coal/gas in industries; road sweeping |
| Stage II: Poor | 201–300 | Plying restrictions on old vehicles; higher parking fees |
| Stage III: Severe | 301–400 | Construction bans; 50% work-from-home for offices |
| Stage IV: Severe Plus | 401+ | Full construction halt; odd-even vehicle rationing; school closures |
Why GRAP-IV Activated on 15 December 2025
AQI in Delhi-NCR hit over 450, entering ‘Severe Plus’ due to stagnant air. Low wind speeds and temperature inversion trapped pollutants during winter. Vehicular emissions (30% of pollution), construction dust, and biomass burning from crop residue worsened the crisis. Seasonal stubble burning in Punjab-Haryana added to the smog.
Key Measures Under GRAP-IV
Transport Restrictions
- Ban on diesel vehicles older than 10 years (petrol >15 years).
- Mandatory 50% electric/CNG buses; odd-even for private cars.
- Metro capacity increased by 20%.
Construction & Industrial Restrictions
- Complete halt on all construction and demolition.
- Closure of polluting industries like stone crushers.
- No coal/gas use in power plants.
Schools, Offices & Public Advisory
- Schools up to Class 11 shift to online/hybrid (Class 10 exempt).
- 100% work-from-home for private offices; 50% for government.
- Health alerts for vulnerable groups: stay indoors, use masks.
Impact of GRAP-IV
Public Health Impact
GRAP-IV protects against respiratory issues, with hospitals reporting fewer cases in past activations. Vulnerable groups like children and elderly benefit most.
Economic Impact
Construction bans affect 10 lakh workers; industries face losses of ₹5,000 crore daily. Small businesses suffer from reduced footfall.
Education & Daily Life Impact
Online classes disrupt learning for 2 crore students. Travel curbs hit daily commuters.
Administrative Challenges
Enforcement strains police resources; violations persist despite fines.
Effectiveness of GRAP – Critical Analysis
GRAP reduced AQI by 20-30% in previous winters, showing short-term success. Limitations include poor inter-state coordination and stubble burning recurrence. It offers temporary relief but needs long-term shifts like clean energy and urban planning.
Way Forward
Adopt tech like real-time AQI monitors and AI forecasting. Policies should promote EV adoption and waste-to-energy plants. Citizens must reduce private vehicles and report violations. Strong air quality governance via National Clean Air Programme is essential.
Conclusion
GRAP-IV on 15 December 2025 underscores Delhi-NCR’s air pollution battle. It enforces immediate action while urging sustainable reforms for health and economy.
For expert UPSC guidance on Environment & Current Affairs, join The Prayas India – Mumbai’s top coaching with daily updates & test series. Visit theprayasindia.com.
FAQs on GRAP-IV and Delhi NCR Air Pollution
Q1. What is GRAP-IV in Delhi NCR?
GRAP-IV is the highest emergency level under the Graded Response Action Plan, activated when air quality enters the ‘Severe Plus’ (AQI 401+) category in Delhi-NCR, triggering strict restrictions on vehicles, construction, and industries to protect public health.
Q2. Why was GRAP-IV activated on 15 December 2025?
It was activated because the AQI in Delhi-NCR crossed 450 due to stagnant winter conditions, low wind speed, temperature inversion, vehicular emissions, construction dust, and biomass/stubble burning.
Q3. Who implements GRAP in Delhi NCR?
The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) coordinates implementation, along with CPCB, state pollution control boards, and local bodies under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Q4. What restrictions come into force under GRAP-IV?
Measures include a complete ban on construction and demolition, closure of highly polluting industries, curbs on older and diesel vehicles, push for public transport, school closures or online classes, and health advisories for vulnerable groups.
Q5. Is GRAP a permanent solution to Delhi’s air pollution?
GRAP is mainly a short-term emergency response to extreme pollution episodes; long-term solutions lie in cleaner fuels, better urban transport, crop residue management, and regional cooperation.