Buddhism
Introduction:
The 6th Century BC saw a rise of many heterodox sects. It is said that as many as 63 heterodox sects were formed during this time period. Out of these 63 sects, Buddhism and Jainism were the two major sects that came to the forefront and laid down a solid foundation which exists till date.
Causes for the Rise of these Sects:
One of the most prominent reasons for the rise of these sects was to oppose the Brahmanical dominance in the society. In addition to this, following are some other prominent reasons for the rise of these heterodox sects in India;
- Brahmanical Dominance: In the Later Vedic Age, there were many complex rituals and practices which were advocated by the people belonging to the higher castes. Such practices were not acceptable to the common people. These ceremonies were very expensive and the superstitious beliefs and mantra’s confused the common man. Moreover, the Upanishads were highly philosophical and difficult to be understood by the common man. Thus, the people needed a simple way of attaining salvation. This simple path was shown by these heterodox sects, especially Buddhism and Jainism.
- Social Factors: The rigidity of the Caste System, especially in the Later Vedic Age restricted certain rights for the lower classes. For instance, certain religious ceremonies could only be performed by the Brahmins i.e., priesthood now became a profession (a hereditary one) which could only be practiced by the Brahmins.
- Growth of Trade: Increase in agricultural production and an increase in trade improved the economic conditions of the Vaishya’s. As a consequence, they wanted to improve their social status as well. However, the rigid caste system did not allow them to raise their social status.
These newly formed heterodox sects, provided a platform which addressed the above issues faced by the common people. Thus, in the 6th century BCE, these sects, especially Buddhism and Jainism raised to prominence.
Early Life of Gautam Buddha:
Gautam Buddha, was born as Siddhartha in 563 BCE at Lumbini in Nepal. He was born in the Sakya clan. His father was Suddodhana and his mother was Mahamaya who unfortunately died at the time of his birth. He was raised by his step-mother Gautami. At the age of 16, he was married to Yashodhara and had a son named Rahul.
At the age of 29, it is believed that Siddhartha saw an old man, a sick man, a corpse and an ascetic. This picture turned him away from the material life. He left his home in the search for truth and wandered for 6 years along-with his companions Vappa, Assaji, Mahanama, Bhaddiya and Kondanna. Siddhartha earlier believed that the practice of extreme austerities would lead to enlightenment. However, this myth of Siddhartha was soon broken when his health deteriorated. One day, on their arrival in a village named Senani, Siddhartha was offered a bowl of rice and milk by a girl named Sujata. After accepting this food, Siddhartha was left deserted by his companions. Herein, Siddhartha sat under a Bodhi tree and took a vow that he shall not get up until and unless he attains enlightenment.
The Story of Mara and attainment of Enlightenment (Nirvana):
Mara was a lord of illusion who tried to break Siddhartha’s vow of attaining enlightenment under the Bodhi tree. However, Siddharta’s wisdom and compassion helped him transform Mara’s weapons into flowers.
Thus, at the age of 35, Siddharta finally attained Nirvana under the Bodhi tree at the banks of river Niranjana. He then came to be called as Buddha – the enlightened one.
Buddha delivered his first sermon at Sarnath. This event is known as “Dhamma Chakka Pavattana”.
He died at the age of 80 at Kusinagara. This event is known as “Mahaparinirvana”.
Buddhist Symbols related to Buddha’s Life:
| Event | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Birth | Lotus and Bull |
| Mahabhiniskramana (The Great Departure) | Horse |
| Nirvana (Enlightenment) | Bodhi Tree |
| Dhammachakkaparivartan | Wheel |
| Mahaparinirvana (Death) | Stupa |
Doctrine of Gautam Buddha:
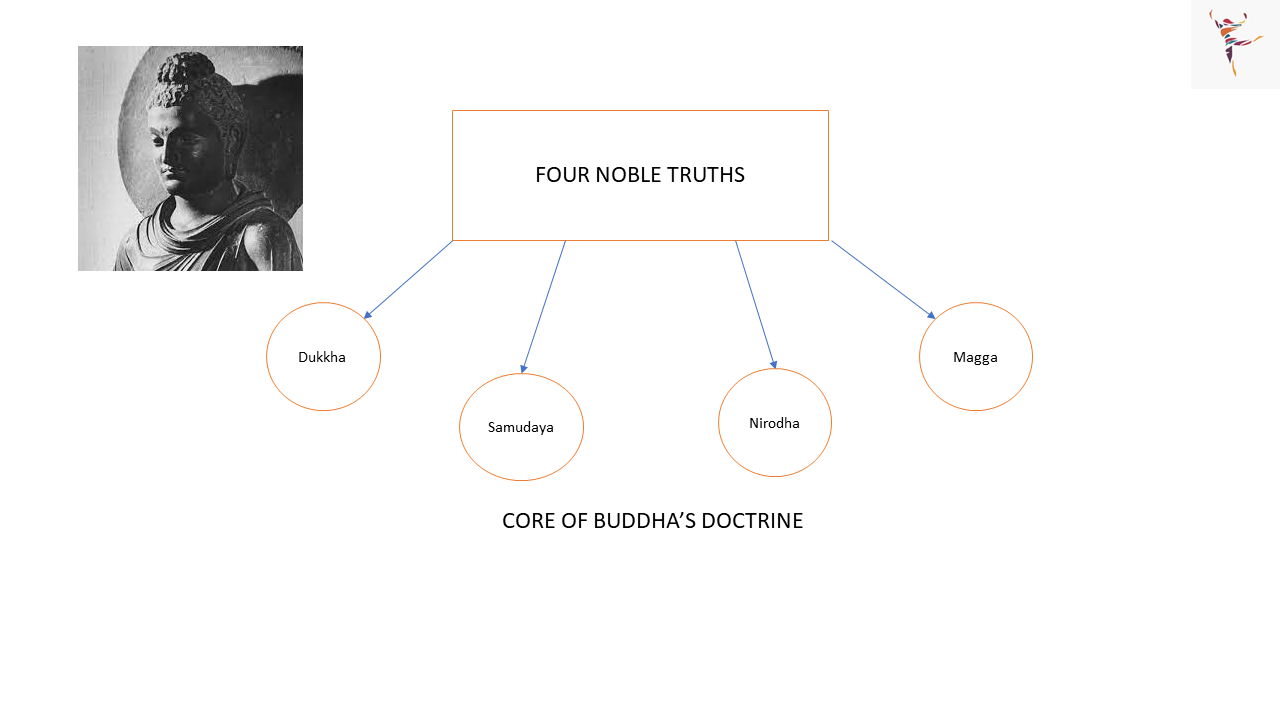
Buddha held a belief that the world is full of suffering. For him, the root cause of suffering was desire to get something. Hence, in order to end this suffering Buddha propagated that an individual needs to overcome his/her desires. In order to overcome these desires, Buddha put forth a noble eight-fold path theory, also known as the “Ashtangika Marga“.
Dukkha: Truth of suffering.
Samudaya: Truth of the cause of suffering
Nirodha: Truth of the end of suffering
Magga: Truth of the Path
Buddha’s Eightfold Path:
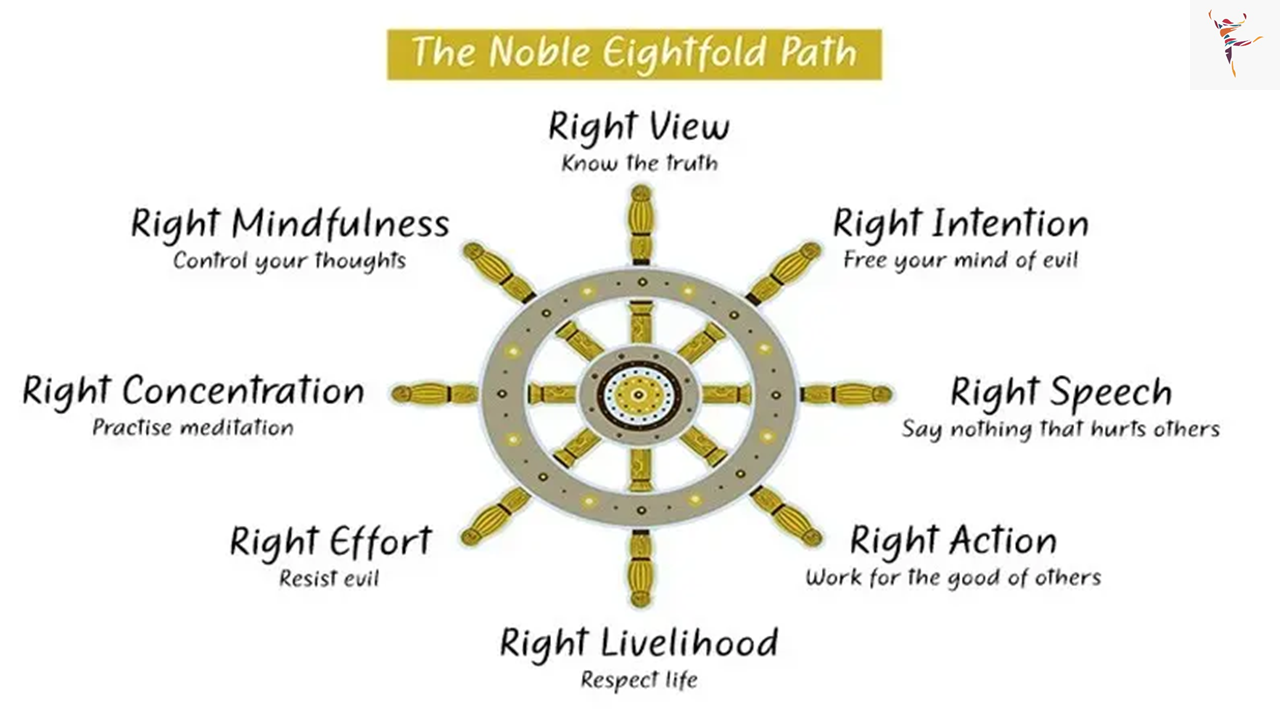
Gautam Buddha rejects the idea of existence of God. Buddhism does not believe in the notions of purity and pollution of the Caste System. The Buddhist Sangha was open for all people irrespective of their caste. Even women were allowed to be a part of the Buddhist Sangha.
Buddhist Councils:
| Buddhist Council | Year | Place | King | President | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | 483BC | Rajgriha | Ajatshatru | Mahakashyap | Composition of Sutta Pitaka and Vinaya Pitaka |
| Second | 383BC | Vaishali | Kalashoka | Sabakami | Lead to the division of Buddhism into two sects: Sthaviravadin and Mahasangika |
| Third | 250BC | Patliputra | Ashoka | Mogliputta Tissa | Lead to the composition of Abhidhamma Pitaka. |
| Fourth | 1st Century AD | Kashmir | Kanishka | Vasumitra | Buddhism got divided into Mahayana and Hinyana sect. |
Schools of Buddhism:
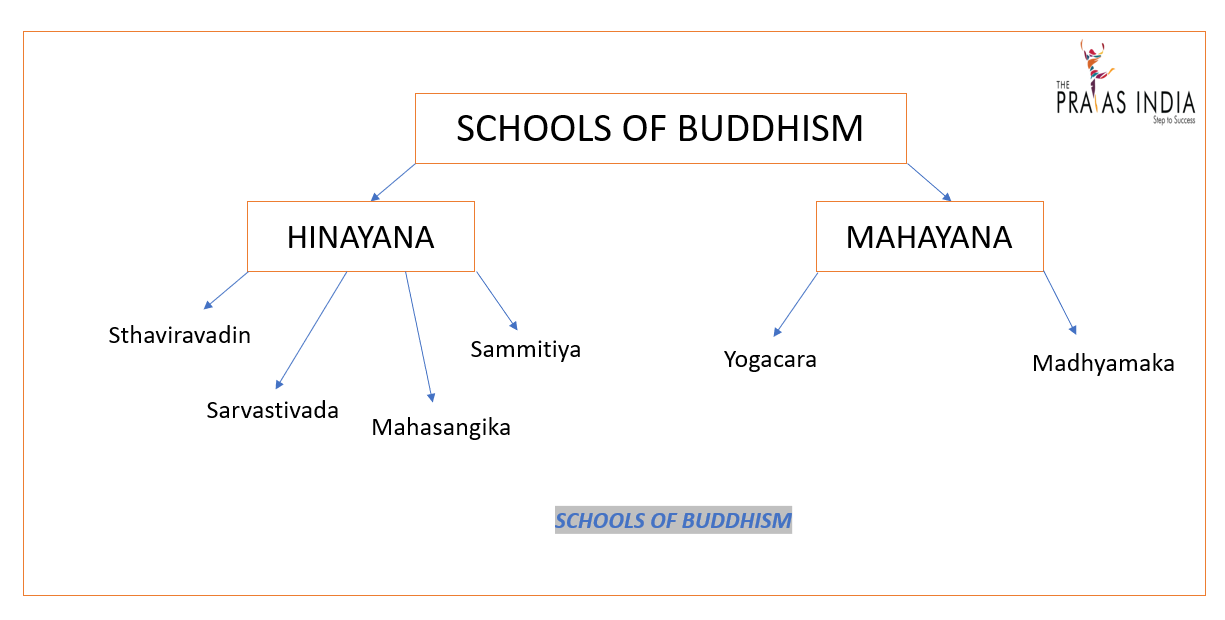
Difference between Hinayana and Mahayana:
| Hinayana | Mahayana |
|---|---|
| Literal meaning – The Lesser Path | Literal meaning – The Greater Path |
| It treats Buddha as a simple human-being. | It treats Buddha as equal to God. |
| Does not believe in idol worship. | It believes in idol worship. |
| Its scriptures are in Pali. | Its scriptures are in Sanskrit |
| At present found in SriLanka, Myanmar and Thailand | At present found in China, Mongolia and Korea. |
| Ashoka patronised this sect. | Kanishka patronised this sect. |
Buddhist Texts:
The Tripitaka’s lay down the basic principles and tenets of Buddhism. These three pitakas are;
- Sutta Pitaka – It tells about the basic teachings of Gautam Buddha. It is divided into 5 parts or Nikayas. It is believed to have been compiled by Ananda, the disciple of Buddha.
- Vinaya Pitaka – It lays down the rules of the Buddhist Sangha. It is believed to have been compiled by Upali.
- Abhidhamma Pitaka – It talks about Buddhist philosophy and its principles.
Apart from the Tripitakas, the followings are some texts/works of Buddhism;
- Vishuddhimarga – It is written by Ashvaghosha.
- Mahavastu (by Hinayana sect) and Lalitvistara (by Mahayana sect) are biographies of Buddha.
- Milindapanho (Questions by Milinda) is a dialogue in the Pali language consisting of a conversation between Indo-Greek king Melander and the monk Nagasena.




![Prayas-तेजस [UPSC CSE Sociology Optional] – Online & Offline](https://theprayasindia.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Prayas-तेजस-UPSC-CSE-Optional-Subject-The-Prayas-India-300x300.png)
![Prayas-सूत्र [UPSC CSE Materials (Hardcopy)]](https://theprayasindia.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Prayas-सूत्र-UPSC-CSE-Study-Materials-Hardcopy-The-Prayas-India-300x300.png)
![Prayas-मंत्रा [UPSC CSE CSAT]](https://theprayasindia.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Prayas-मंत्रा-UPSC-CSE-CSAT-The-Prayas-India-300x300.png)
![Prayas सारथी [UPSC CSE One on One Mentorship]](https://theprayasindia.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Prayas-सारथी-UPSC-CSE-One-on-One-Mentorship-The-Prayas-India-300x300.png)











